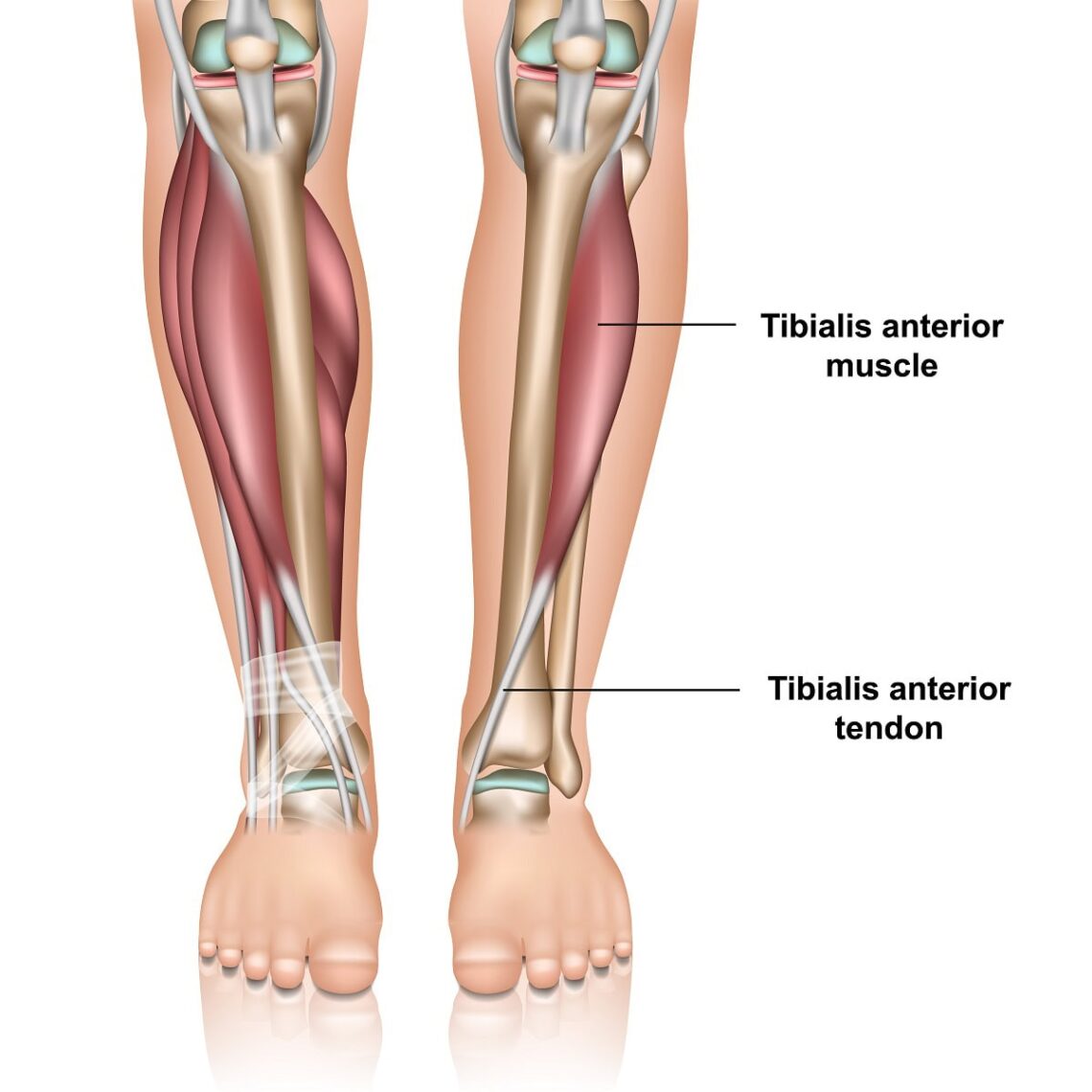
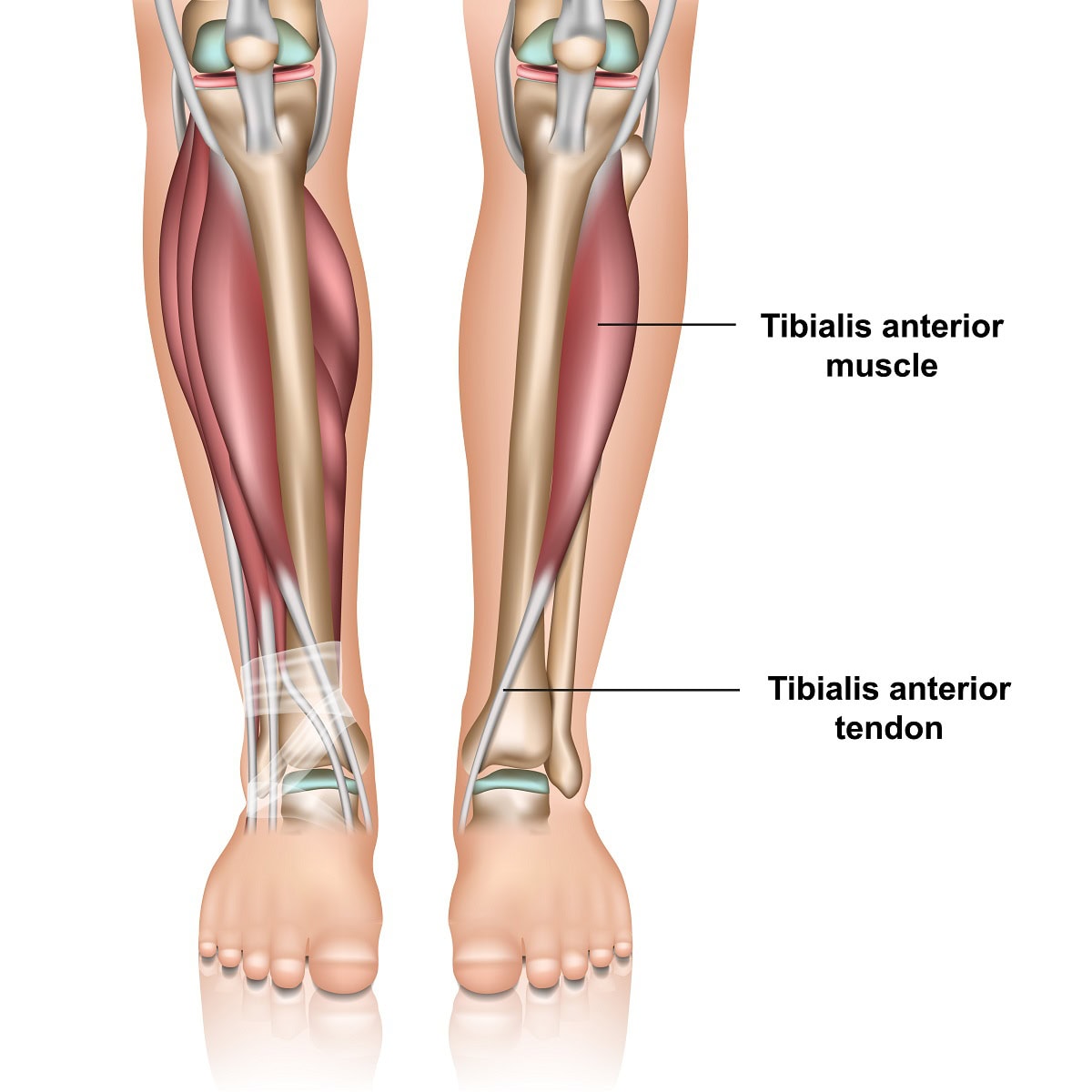
The foot has several tendons that originate in the lower leg and extend into the foot. They each have different functions to stabilize the foot and help us to propel our bodies forward when we walk or run. The anterior tibial tendon is one of these tendons. Although tibialis anterior tendonitis may be the least common complaint of those experiencing tendon pain around the ankle joint, it’s important to understand how to recognize and what can be done to eliminate your pain.
Anatomy and function- The anterior tibial tendon is the third largest tendon in the foot and ankle. The largest is the Achilles tendon and the second largest is the posterior tibial tendon. The anterior tibial tendon originates as a muscle in the lower leg adjacent to the shin, tibia, and extends down to the foot. It is on the front of the ankle. It inserts onto the top and inner side of the arch.
Its function is to pull the foot up and support the arch. It also assists in supinating the foot. Supination is a motion often referred to and means that the arch of the foot increases and the foot angles towards the opposite foot. Finally, it decelerates the downward motion of your foot towards the ground. From the time your heel contacts the ground to the point of the ball of the foot bearing weight it prevents your foot from slapping against the ground. So, it’s very important for normal gait to occur. It helps to identify the tendon by pulling your foot up towards you and it will be the tendon that protrudes on the front of the ankle and is running towards the inside of the foot towards the big toe.
Tibialis anterior tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and discomfort along the front of the lower leg and ankle due to inflammation or degeneration of the tibialis anterior tendon. This tendon plays a crucial role in foot movement, particularly in lifting the foot upward while walking or running.
Where Will The Pain Be If I Have Tibialis Tendonitis?
It is most common towards the front of the ankle area. The symptoms of tibialis anterior tendonitis may also create pain above the ankle in the lower leg adjacent to the tibia. This may be referred to as anterior shin splints. Referring to shin splints on the front of the leg. Symptoms may also be closer to or at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot on the inner side of the arch.
What Causes Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis?
Several factors can contribute to tibialis anterior tendonitis, including:
- Overuse – this may occur from doing too much too soon which can happen in any activity. However, any activity that requires you to extend your foot in front of the knee joint may increase the probability of overuse. Examples of this may be racquet sports, hiking, or running downhill.
- Biomechanics – If your born with a flat foot the tendon may have to work harder to help support your arch.
- Improper running technique – Over striding while running can also cause overuse of the tendon. By taking shorter strides you won’t be extending the foot in front of you as much as this will help to reduce the need for the anterior tibial tendon to stop foot slap.
- Neurological problems – Neurological problems may not cause pain along the tendon, however, may cause damage to the nerves that stimulate the anterior muscle to contract. This is referred to as drop foot. Drop foot can be associated with back issues of a nerve issue around the see. Nerve surgery called decompression surgery can help with this.
- Trauma – a severe ankle sprain could cause a tear to the tendon. Also, a laceration to the ankle area may also cause a partial or full tear.
- Shoe gear – High heels may also be a cause and they will put more demand on the tendon to reduce the potential for foot slap because of the elevation of the heel off the ground.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing unsupportive or worn-out shoes can alter foot mechanics, leading to excessive strain.
Symptoms of Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Common signs and symptoms of tibialis anterior tendonitis include:
- Pain and tenderness along the front of the shin, ankle, or top of the foot.
- Swelling in the affected area, especially near the tendon insertion.
- Weakness or difficulty lifting the foot, potentially leading to a “foot slap” while walking.
- Stiffness and discomfort that worsens with activity, particularly when walking downhill or running.
- Pain when pressing on the tendon or flexing the foot upward against resistance.
Diagnosis or Evaluation of Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
A podiatrist will typically diagnose tibialis anterior tendonitis through:
- Clinical Examination: The physical examination alone will give the doctor a good idea if the tendon is damaged. There will be pain and swelling along the tendon or its muscle higher up the leg. Also, weakness of the tendon may be noted.
- X-rays – these will not show tendon damage but are useful to rule out other problems.
- Diagnostic Ultrasound: Assessing the tendon’s structure and detecting any tears or degeneration.
- MRI Scan: MRI scans or diagnostic ultrasound are useful to confirm the diagnosis and see the extent of the tendon damage. The diagnosis will frequently be tibialis anterior tendinopathy. The tendon may be damaged but not torn.
- Gait Analysis: Observing walking patterns to detect abnormalities such as foot drop or imbalance.
Treatments for Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Most cases of tibialis anterior tendonitis can be managed with non-surgical treatments, including:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing strain by limiting high-impact activities.
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help relieve symptoms.
- Immobilization: Wearing a CAM walker or brace to reduce movement and promote healing.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom arch supports to help alleviate stress on the tendon.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching, strengthening exercises, and modalities like ultrasound therapy can aid recovery.
Advanced and Surgical Treatments
For severe cases where conservative measures are ineffective, the following treatments may be recommended:
- Laser Therapy: Multiwave laser (MLS laser) MLS treatments have shown success in reducing pain and inflammation.
- Human Cellular Tissue Products: Also known as stem cell therapy, these injections can promote tendon healing. This treatment has significantly reduced the chance of surgery when partial tears are noted. It is important to note that in many cases the tendon may not be inflamed as much as it is breaking down. This is sometimes referred to as tendinosis rather than tendonitis. For this reason, regenerative medicine is very appropriate as it helps to repair the tendon.
- Corticosteroid Injections (With Caution): While cortisone injections may provide short-term relief, excessive use can weaken the tendon and increase the risk of rupture.
- Surgical Repair: If a partial or full tear is noted surgery to repair the damage may be recommended. With a full tear weeks of non-weight bearing may be needed. In cases of complete tendon rupture or severe degeneration, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore function. Post-surgery, a period of non-weight-bearing followed by rehabilitation is typically required.
How to Avoid Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis?
It’s important when taking up a new activity to not do too much too soon. Also, if you suffer from flat feet, make sure you have supportive shoes or consider over-the-counter arch supports or custom-made orthotics.
Hopefully this blog will help you to better understand if you have tibialis anterior tendonitis and how some of the newer treatments available including regenerative medicine and laser treatments can help manage the condition. Our foot and ankle clinics cater to patients from Colorado, Wyoming and Nebraska. We also see patients from all over the United States and even our neighbors from Canada who have searched for a ‘expert podiatrist near me‘. Watch our patient testimonials on YouTube as we now have over +11000 followers.
For expert evaluation and treatment, schedule an appointment with Anderson Podiatry Center today.





Write a comment: