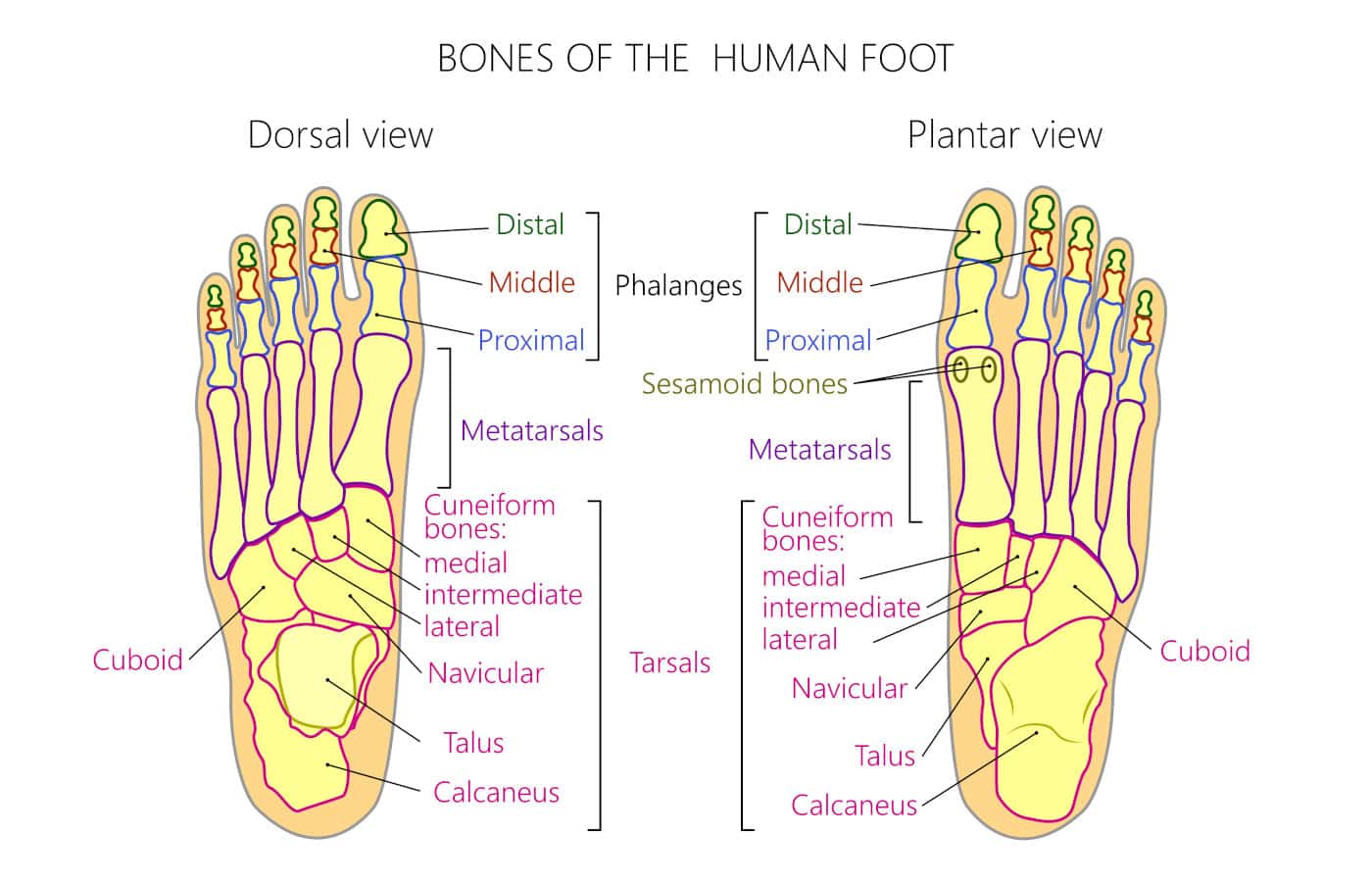
There are many bones in the foot making its anatomy one of the more complex in your body. Of the 26 bones in the human foot approximately half of them are phalanges in the foot. Generally, as we start towards your ankle joint and move down the foot towards the toes the number of bones become more multiple in the distal extremity. For example, in your rearfoot there are two large bones the talus (ankle bone) and calcaneus (heel bone) and 14 phalanx bones. The anatomy of the hands and feet are similar but because you walk on your feet one could argue they are more of a structural wonder. We will describe the anatomy of these bones and potential issues that could cause pain in this area of your foot.
Basic anatomy of phalanges in the foot
The phalanges are the bones of the foot that comprise the bone of your toes. They are connected to the larger and longer metatarsal bones that extend from the midfoot down to the ground forming the ball of your foot. When you bear weight on the ball of the foot you’re standing on the metatarsal heads on the plantar surface of these long bones. The phalanges extend beyond the ball of the foot forming the digits. They are comprised of the proximal, middle and distal phalanges.
Proximal phalanges of the feet
These bones form the articulation with the metatarsal bone These two bones form the metatarsal phalangeal joints. These five joints that form the ball of your foot have a lot of upward mobility called dorsiflexion. This allows these joints to bend upwards to allow you to pivot up onto the ball of the foot when you walk or run. The anatomy of these joints is very complex as they require various tendons and ligaments to maintain their stability. This is especially true for the great toe joint. This has beneath it two bones called sesamoid bones that glide beneath the great toe joint as the toe moves up and down, much like your kneecap. The function to improve leverage and therefore strength to the great toe joint as this joint is important to assist in propelling us forward when walking or upward when we jump.
Intermediate phalanges
The next phalangeal bones as we move away from the ball of the foot are the intermediate phalanges. They may also be called the middle phalanges as they lie in the middle of the toes. They are smaller than the proximal phalanges bones. As was just mentioned the great was unique as it has two bones beneath it called the sesamoid bones and there is one more difference with the great toe. The great toe only has two phalanx bones. They are referred to as the proximal and distal phalanx bones.
Distal phalanges
At the very end of each toe are the distal phalanges. These are the smallest of the phalanges and lie beneath the toenails. Rather than having a tubular shape like the proximal and intermediate phalanges they are short and triangular shaped.
The joints of the toes.
We had mentioned earlier that the joint formed by the metatarsal bones and the proximal phalanges is called the metatarsal phalangeal joint.
- The joint formed by the proximal and intermediate phalanx is called the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ).
- The joints formed by the intermediate phalanx and the distal phalanx are called the distal interphalangeal joints (DIPJ).
- Finally, the great toe must be different as it only has two phalanges, so it does not have a proximal and distal interphalangeal joint. Because it has only two phalanges its joint between these two bones is called the interphalangeal joint.
- Finally, the great toe also has its name, referred to as the Hallux.
To summarize the big toes are different in three ways
- It has only two phalanx bones.
- It has two sesamoid bones beneath it at the metatarsal phalangeal joint.
- It has its own name, Hallux.
Functions of the phalanx bones in the foot
These appendages help with your balance and push your foot off the ground when you walk, run, or jump. The great toe is more important for these purposes than the other four toes. It’s important to note that in a situation of an amputation of a digit. Removal of one of the smaller toes will have little effect on your balance and ability to function normally. However, the absence of the great toe has more impact.
Problems that can arise in the phalanges
Since these bones are the distal extremities of the foot, they can be subject to trauma such as stubbing your toe. When this happens you may fracture a phalanx bone. Contrary to the popular notion that nothing can be done it’s important to have the injured toe evaluated. Why? If a fracture is present a common treatment will be to buddy tape the injured toe to an adjacent toe. This is important during the healing phase to ensure the fracture does not get too displaced. A fracture that heals in a misaligned position can create long-term pain and require surgical intervention. When the great toe is fractured, proper evaluation is needed to ensure proper healing because of its importance for normal ambulation. Again, proper treatment and follow-up is important.
Hammertoes
Hammertoes are deformities of the digits and can create pain from the dorsal surface of the toe rubbing shoe gear of the walking surface. There are three types of hammertoes
Mallet toe. This deformity is at the distal interphalangeal joint. The metatarsal phalangeal joint and proximal interphalangeal joint are in good alignment; however, the distal interphalangeal joint is flexed downward.
Claw toe. This deformity involves all the joints. The metatarsal phalangeal joint is flexed upwards, and the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints are flexed downward. The bases of the middle phalanx may rub shoe gear.
Hammertoe this deformity involves two joints. The metatarsal phalangeal joint is flexed upwards, and the proximal interphalangeal joint is flexed downward.
Treatment for hammertoes is
- Conservative – wearing appropriate shoes with bigger toe box, padding, etc.
- Surgery – Foot Surgery is performed to realign the digit to its normal position.
Hopefully, this blog has given you more insight into the phalanx bones, their anatomy, and problems you may encounter in this region of your foot. If you are seeking a ‘podiatrist near me’ in Broomfield or Fort Collins, consider Anderson Podiatry Center. We have our own surgical foot center that has many advantages which you can review here.
Call us today at our Fort Collins location (970) 329-8158, Broomfield location (303) 997-2795, Surgery Center (970) 329-8158, or use our online scheduling system to book your appointment.


