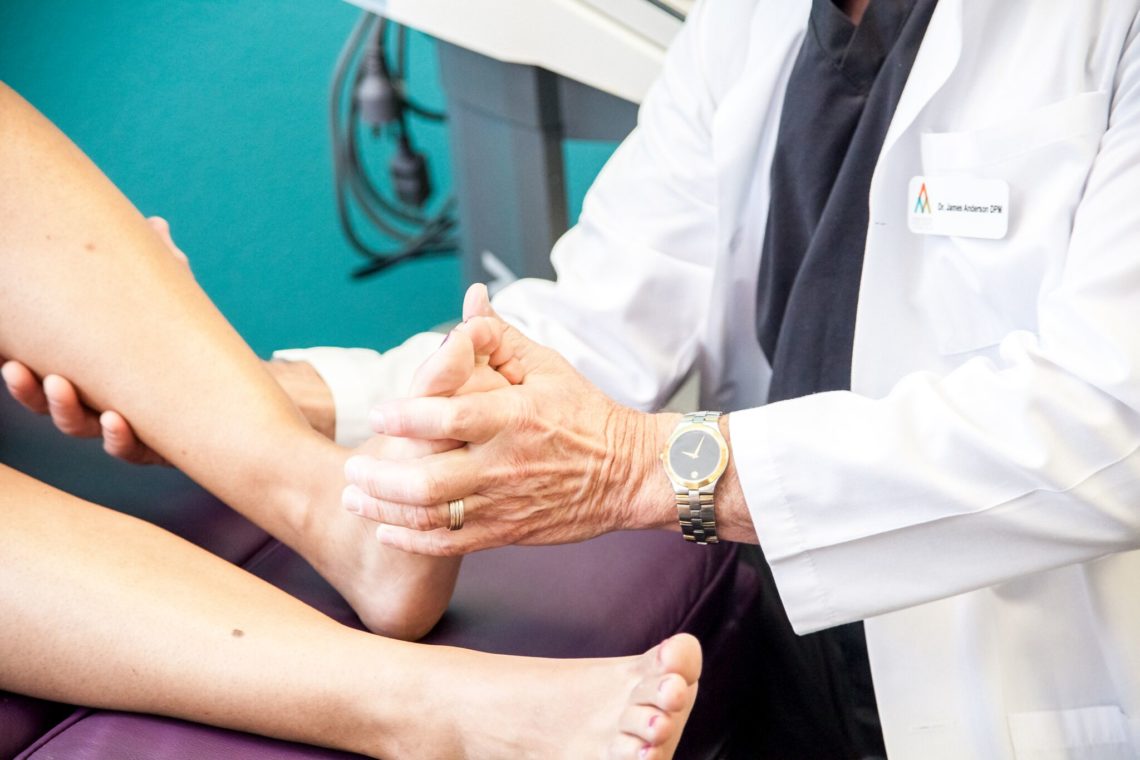
In Part 1 of this blog series, we talked about the symptoms, locations and causes of neuropathy. Today, we will discuss the treatment options available. First, I would like to address the approach that many patients experience with conventional medicine. Next, we will talk specifically about our approach, and the treatment options we use that have shown to have a high success rate in patients suffering from neuropathy. Let’s jump in.
The Pharmaceutical Approach
In conventional medicine today, it has become very commonplace to treat neuropathy with medication. I call this the pharmaceutical approach. Medications that are typically prescribed can include Lyrica, Neurontin and Gabapentin.
While these can have some positive impact, the side effects are often what patients struggle with. They can start to feel spacey, and also gain weight. Although the average weight gain is between 10-15 pounds, I have seen some patients gain as much as 40-60 pounds taking these medications. In severe cases, sometimes patients resort to taking narcotics for pain relief, and then there is the risk of opiate addiction.
Is it Coming From Your Back?
The second approach I typically see is that patients have heard the primary cause of their symptoms is coming from their back. They come to us and are often confused. They say, “I went to one doctor and they said my nerves are diseased, and then I went to another doctor and they said it’s coming from my back.”
Many times these patients have been told all they can do is live with it or take medication. If they have been told it’s coming from their back, they might look into chiropractic care, physical therapy, injections, or even surgery.
Our Approach
Our approach is different. We look at the lower limb much like you would look at the upper limb. There are nerve tunnels in the lower extremity that can become compressed or damaged. And the good news is that this gives us the opportunity to reverse the symptoms of neuropathy. Depending on the patient’s exam results and symptoms, we have both surgical and non-surgical treatment options available.
Nerve Decompression Surgery
This is a minimally-invasive, 1-hour procedure. We go in surgically to open up nerve tunnels in the patient’s leg that have become compressed. When we release the pressure from the nerve, patients often see up to 90% improvement from their symptoms. Whether they have diabetic neuropathy, non-diabetic neuropathy, or even chemo-induced neuropathy, we typically see a high success rate with this treatment option. This is also most appropriate for patients with very severe neuropathy symptoms.
ESTIM Treatment
This is a non-surgical treatment option. ESTIM is an electrical stimulation treatment. We use this on the nerves, and send various pulse waves into the anatomy of the leg. This can stimulate the nerves to want to repair themselves. Studies have shown increased nerve repair, and demonstrated how small nerve endings come back to life after ESTIM treatment.
MLS Laser Treatment
This is also a non-surgical treatment option, and it works more on the cellular level. The mitochondria is the “energy-creating” part of your cells. The laser works by targeting the mitochondria specifically in the nerve cells to help repair the damaged nerve tissue.We often use ESTIM and MLS Laser treatment in combination because it can be very effective in providing relief to a patient suffering from nerve pain.
My goal in sharing these treatment options with you is ultimately to instill hope. I find that most patients suffering from severe neuropathy struggle to keep hope alive.
We see patients every day who are finding relief from their neuropathy and nerve pain after years of suffering. In Part 3 of this blog, I will share some of these patient success stories with you. Stay tuned! You don’t want to miss it.
To learn more about how we treat neuropathy, click here .
Part three of this blog post can be viewed at ‘Real Patient Real Stores‘.
To make an appointment, click here.




Write a comment: